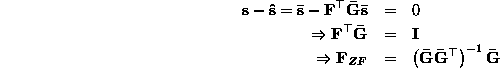
Where
It is important to note that
The zero-forcing receiver is a natural progression of the
decorrelating detector. Now that we have removed the MAI, we want to
eliminate the ISI as well. This can be done by taking into consideration
each users channel impulse response. The vector ![]() developed in
our bit synchronous model includes both the spreading gains and
channel impulse response information of each user. Using this
formulation, we develop the zero-forcing
equalizer,
developed in
our bit synchronous model includes both the spreading gains and
channel impulse response information of each user. Using this
formulation, we develop the zero-forcing
equalizer, ![]() .
.
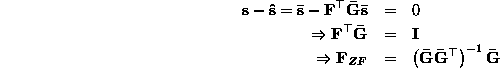
Where ![]() is a matrix of individual
is a matrix of individual ![]() equalizers. To solve for
user k only, we introduce
equalizers. To solve for
user k only, we introduce ![]() , an all zero vector of dimension
matching the stacked source vector with a one in the position
corresponding to
, an all zero vector of dimension
matching the stacked source vector with a one in the position
corresponding to ![]() in the stacked source vector.
So to receive user k, at delay
in the stacked source vector.
So to receive user k, at delay ![]() , we solve,
, we solve,
![]()
It is important to note that ![]() must exist for the zero-forcing solution to
exist. Brown et al. investigate certain necessary conditions for the
existence of the zero-forcing solution in [2].
The zero forcing equalizer is successful at eliminating MAI and ISI, but has
some tradeoffs. An estimation of
must exist for the zero-forcing solution to
exist. Brown et al. investigate certain necessary conditions for the
existence of the zero-forcing solution in [2].
The zero forcing equalizer is successful at eliminating MAI and ISI, but has
some tradeoffs. An estimation of ![]() , which includes
the channel information, users spreading codes and timing, must be
obtained. Also, the zero-forcing equalizer suffers the same noise
enhancement problems as does the decorrelating detector. In order to
improve performance in the presence of noise, we develop the minimum
mean squared error equalizer.
, which includes
the channel information, users spreading codes and timing, must be
obtained. Also, the zero-forcing equalizer suffers the same noise
enhancement problems as does the decorrelating detector. In order to
improve performance in the presence of noise, we develop the minimum
mean squared error equalizer.